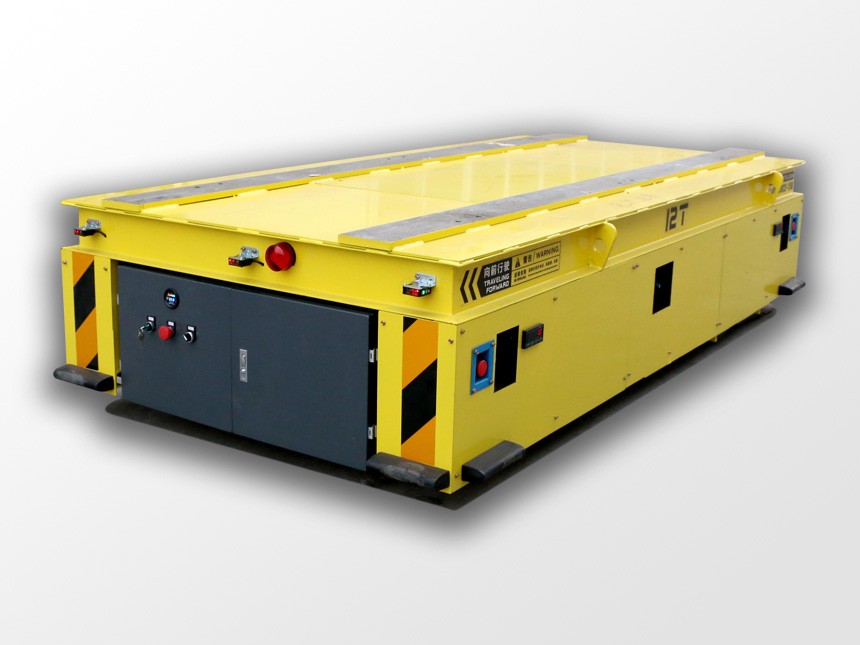
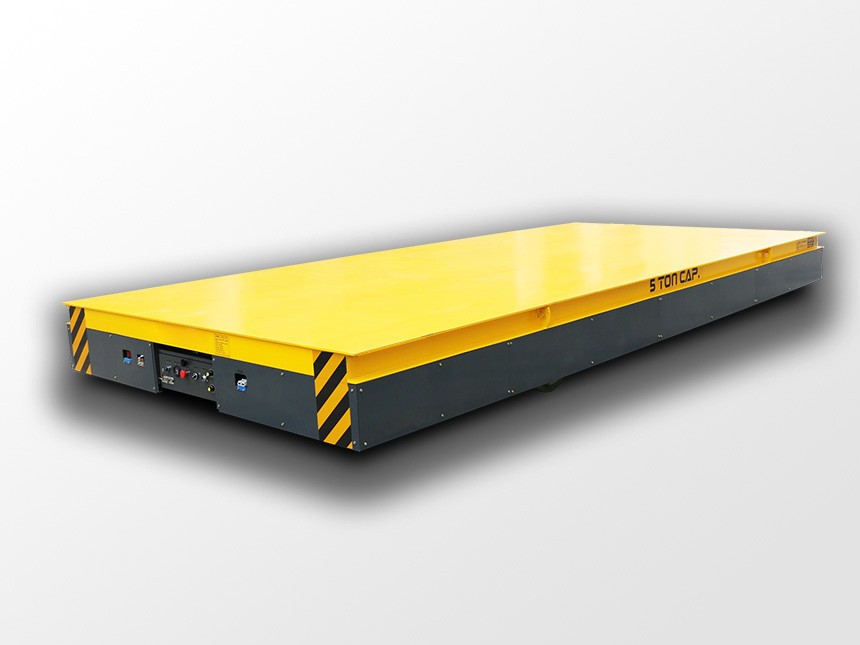
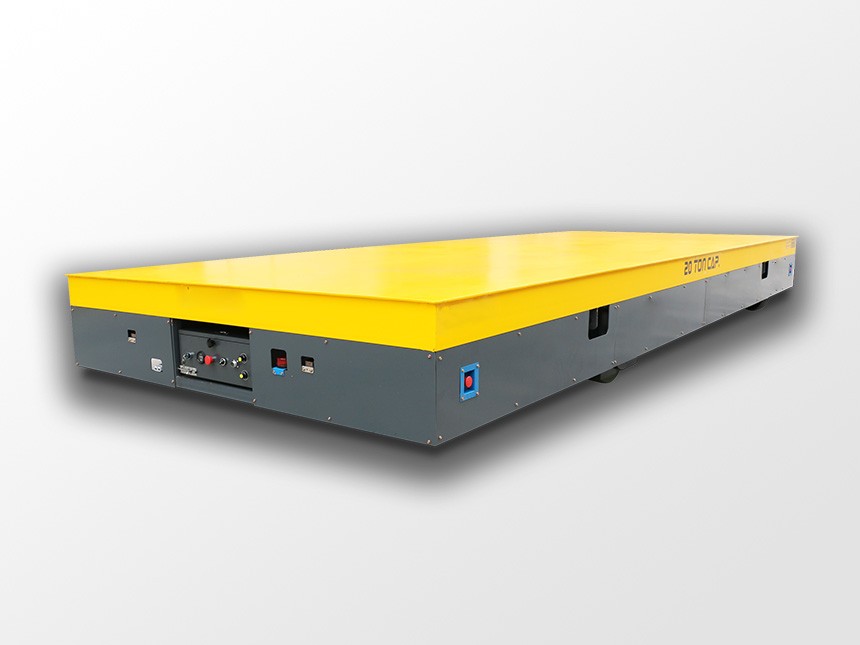
Upgrading to AGVs is one of the most effective ways to modernize internal logistics—but only if you choose the right model. With dozens of configurations available today, from compact material movers to ultra-heavy transporters capable of carrying more than 100 tons, the key is selecting a vehicle that truly fits your workflow.
This guide breaks down the essential factors that determine AGV performance in real production environments, helping you avoid under-sizing, bottlenecks, or costly redesigns later on.
Why the “Right AGV” Matters More Than You Think
Your AGV choice influences far more than transport efficiency. It directly affects:
Overall production throughput
Workplace safety
Energy consumption
Maintenance frequency
Equipment longevity
Long-term scalability
A vehicle that is too slow, too weak, or not suited to your operating environment can quickly become a source of delays instead of productivity.
Load Capacity: The Starting Point for Any AGV Selection
Load capacity is always the first specification to confirm, because it defines the AGV’s structural design, motor size, battery requirements, and speed.
Common Load Segments in Industrial AGVs
Light-duty (≤1–2 tons)
Ideal for electronics, small parts, assembly materials, packaging, and line-side totes.
Medium-duty (2–10 tons)
Used for machining components, steel parts, warehouse pallets, and assembly fixtures.
Heavy-duty (10–100+ tons)
For molds, wind turbine components, metal coils, power-generation equipment, and large industrial assemblies.
ATN’s core strength lies in this segment, with precise and stable heavy-load transporters.
How to Determine the Load You Actually Need
Calculate total transport weight, including:
Product/material weight
Pallet or fixture
Any top module (lift table, roller deck, turntable, etc.)
Safety margin (typically 20–30%)
Example:
Material: 6 tons
Pallet: 1 ton
Lifting module: 0.8 ton
→ Actual load: 7.8 tons
→ Recommended AGV rating: 10 tons
The safety margin protects motors, extends battery life, and keeps long-term operation stable.
Travel Speed: Finding the Right Balance Between Throughput and Safety
AGV speed isn’t simply “the faster, the better.”
Speed must be aligned with your load weight, aisle width, and traffic conditions.
Typical Speed Ranges
Light-duty: 1.0–1.5 m/s
Medium-duty: 0.8–1.2 m/s
Heavy-duty: 0.4–1.0 m/s
(Heavier AGVs run slower due to braking distance and stability requirements.)
What Affects the Speed You Should Choose
Width and straightness of aisles
Pedestrian activity
Number of turns or intersections
Floor quality
Hourly throughput targets
Congestion or equipment density
For long transport loops or time-critical operations, a higher-speed model may be necessary to maintain cycle time.
Battery Systems: Powering AGVs for Real Operations
Battery technology controls how long your AGV runs, how often it charges, and how much maintenance is required.
Lead-Acid (Traditional)
Pros:
Low cost
Stable, proven
Suitable for light workloads
Cons:
Long charging times
Shorter lifespan
Requires regular maintenance
Best for simple operations with low duty cycles.
Lithium-Ion (Modern Standard)
Pros:
Fast charging
High energy density
Long service life
Zero daily maintenance
Strong performance in 24/7 production
Cons:
Higher initial investment
Most modern AGVs use lithium batteries because they offer predictable performance and excellent ROI.
Supercapacitors (Ultra-Fast Charging)
Pros:
Charge in 1–5 minutes
Extremely long cycle life
Ideal for workflows with short stops
Cons:
Lower energy storage
Suited for short, repetitive tasks
Supercapacitor AGVs are common in high-frequency shuttle systems.
Operation Mode & Workflow Integration
The right AGV must match not only your load but also how your production line actually works.
Levels of Automation
Manual / Remote-control — simple movement, low cost
Semi-automated — guided operation with sensors
Fully automated — integrated with MES/WMS/ERP for end-to-end automation
Top Modules That Change AGV Functionality
Lifting platforms
Roller or conveyor decks
Rotating tables
Robotic interfaces
Forklift attachments
Custom fixtures
In many projects, the module on top of the AGV is just as important as the AGV chassis itself.
Environmental Compatibility: Don’t Overlook These Factors
A well-performing AGV must match the physical conditions of your facility.
Flooring
Concrete
Epoxy
Steel plates
Grating
Uneven surfaces
Heavy-duty AGVs may need custom suspension or reinforced drive systems.
Temperature Requirements
Cold storage down to –25°C
High-temperature environments near furnaces
Cleanrooms requiring anti-static components
ATN supplies AGVs specifically engineered for these conditions.
Aisle Width & Turning Radius
The vehicle must safely navigate:
Narrow aisles
Sharp turns
Multi-intersection routes
Loading/unloading points
Heavy AGVs often rely on omni-directional or multi-steering axles for tight layouts.
Navigation: Matching Technology to Your Layout
You can choose from several navigation systems, each suited to different workflows:
Magnetic tape: cost-effective for stable routes
QR/visual: flexible and easy to update
Laser (LIDAR): high precision, easy to reconfigure
Inertial: excellent for harsh or vibration-heavy environments
Hybrid: combines strengths for complex, multi-zone layouts
Navigation is a long-term decision—choose for accuracy, scalability, and maintainability.
How to Build a Complete AGV Requirement Sheet
Before purchasing, prepare a clear technical brief. Key items include:
Load weight & dimensions
Center of gravity
Route layout (or CAD drawing)
Required cycle time
Navigation preference
Charging strategy
Environmental details
Safety requirements
Integration needs (MES, sensors, conveyors)
Future scalability
ATN engineers often work with customers directly to create this document during the planning phase.
ATN AGV Solutions for Every Industry
ATN provides:
Light, medium, and heavy-duty AGVs
Trackless and track-guided transporters
Omni-directional heavy carriers
Cleanroom and cold storage AGVs
Fully customized AGV designs
Complete automated logistics engineering
Our solutions support customers in more than 48 countries across automotive, electronics, steel, energy, heavy equipment, and general manufacturing.
Learn more: https://www.atnagv.com
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right AGV is far more than choosing a model from a brochure.
It requires understanding your load characteristics, route demands, battery strategy, navigation needs, and environmental limitations.
When done correctly, a well-matched AGV system can dramatically increase productivity, reduce labor dependency, and create stable, scalable logistics for years to come.

 English
English 简体中文
简体中文


